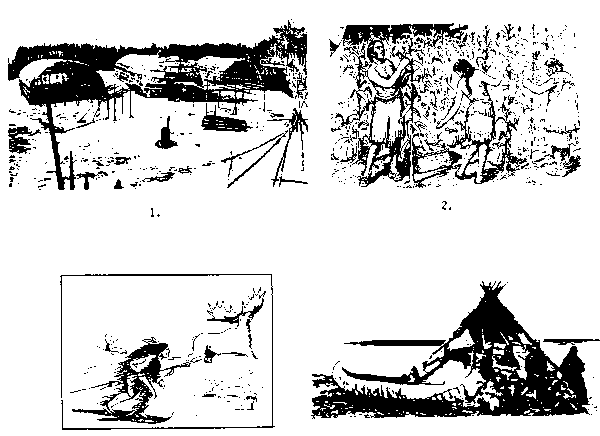
 7. Which of the following
diagrams illustrate the way of life of the Algonquins who lived mainly
north of the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands?
7. Which of the following
diagrams illustrate the way of life of the Algonquins who lived mainly
north of the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands?
UNIT 3: AMERINDIAN CIVILIZATION
TOPIC A: SOCIO-CULTURAL ORGANIZATION
TOPIC B: MUTUAL INFLUENCES
1. Which of the following four texts describes an aspect of the way of life of the ALGONQUIN during the 16th and 17th centuries?
a - These Amerindians depended mainly on agriculture for their livelihood. They grew corn, beans and various types of squash.
b - These Amerindians lived in small bands. Each band had a chief,but he had little authority. They lived in wigwams and frequently migrated in search of game.
c - These Amerindians lived in longhouses, where the woman gave shelter to her husband. The longhouse also sheltered the woman's mother, her sisters, and their families.
d - These Amerindians lived in the St. Lawrence Lowlands, mainly in fortified villages of more than 500 people each.
A)
B)
C)
D)
2. The Mohawk crisis that shook Quebec during the summer of 1990 demonstrated THE ROLE PLAYED BY WOMEN in the Iroquoian community.Even before New France was settled, Iroquoian women occupied a place of primary importance in the matriarchal society.Which two of the following describe the roles played by women in Iroquoian society?
1- They elected the chiefs.
2- They were responsible for cultivating the fields.
3- They were the shamans (priests) of the village.
4- They went to live in their husbands' wigwams.
5- They hunted and fished to feed the family.
6- They took part in war-making decisions.
A) 1 AND 4
B) 2 AND 6
C) 3 AND 5
D) 1 AND 6
3. Which of the following describe the NOMADIC way of life of the ALGONQUINS?
1. They depended on agriculture for their main source of food.
2. Their homes consisted of birchbark tents called wigwams.
3. Their villages were protected by fortifications.
4. Their principal economic activities were hunting and fishing.
5. Their pottery was plentiful and well developed.
6. Their social and political organization was basic in structure.
A) 1, 2, and 6
B) 1, 3, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 2, 4, and 6
4. Which of the following best describe the Algonkian way of life?
1. nomadic lifestyle
2. matriarchal society
3. economy based on hunting and fishing
4. economy based on agriculture (corn)
5. wigwam villages
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 1, 3, and 4
C) 1, 3, and 5
D) 2, 4, and 5
5. Which of the following describe the sedentary way of life of the Iroquois?
1. They depended on agriculture for their main source of food.
2. Their homes consisted of small birch-bark tents called wigwams.
3. Their villages were protected by fortifications.
4. Fishing and hunting were their main activities.
5. Their pottery was plentiful and well developed.
6. They lacked social and political structures.
A) 1, 3, and 5
B) 1, 4, and 6
C) 2, 3, and 4
D) 2, 5, and 6
6. Three of the following sentences describe the nomadic characteristics of the Algonkian way of life.Identify them.
1. They lived in tents covered with bark and animal skins.
2. Their food was produced mainly by hunting and fishing.
3. Their villages were surrounded by wooden stockades.
4. Their political structure was very loose.
5. They made and used lots of pottery.
6. They cultivated corn, pumpkins, and beans.
A) 1, 2, and 4
B) 1, 3, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 6
D) 4, 5, and 6
 7. Which of the following
diagrams illustrate the way of life of the Algonquins who lived mainly
north of the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands?
7. Which of the following
diagrams illustrate the way of life of the Algonquins who lived mainly
north of the Great Lakes - St. Lawrence Lowlands?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 4
D) 3 and 4
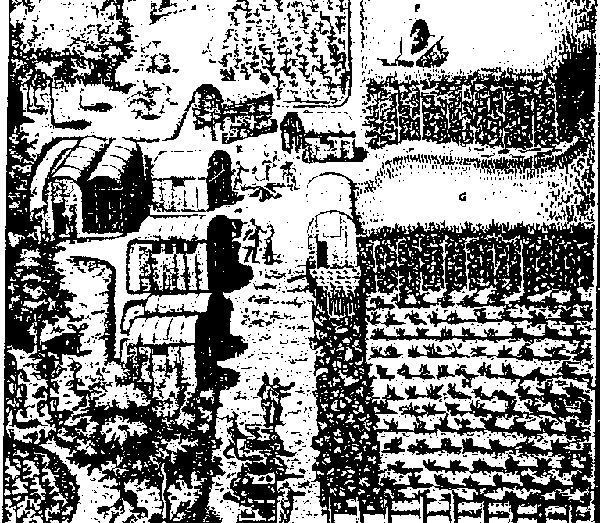 8. Which of the following
can be associated with the Amerindian way of life as illustrated above?
8. Which of the following
can be associated with the Amerindian way of life as illustrated above?
1. sedentary lifestyle
2. wigwam shelters
3. nomadic lifestyle
4. longhouse shelters
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
9. The Algonquins were one of the native groups living in North America at the time of the European exploration.Which of the following can be associated with the Algonquins?
a - They had no fixed villages, but instead moved around a wide area in search of game.
b - The largest villages were fortified with log walls which protected about thirty longouses.
c - The famous totem poles were first fashioned by these Amerindians.
d - In the winter, seal and walrus were their main foods. In the summer,the migrating caribou herds kept them alive.
A)
B)
C)
D)
10. The lifestyle and social organization of the Amerindians was greatly influenced by their natural environment.Which of the follwing characteristics are associated with Iroquois society?
NATURAL REGION
1. the Canadian Shield
2. the St. Lawrence Lowlands
LIFESTYLE
3. sedentary
4. nomadic
SOCIAL ORGANIZATION
5. matriarchal
6. patriarchal
A) 1, 3, and 6
B) 1, 4, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 2, 4, and 6
11. Throughout the 17th century the French colonists in New France were in contact with two large tribes of Amerindians: the Algonquin and the Iroquois.Identify three characteristics of the Iroquois way
of life.
1. The longhouse sheltered several families who were descendants of the same grandmother.
2. Their shelter was a light tent that was easy to put up and to transport.
3. Their principal economic activities were hunting and fishing.
4. Their principal economic activity was agriculture.
5. They lived primarily along the shores of the St. Lawrence River and the Great Lakes
A) 1, 3, and 6
B) 1, 4, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 2, 4, and 6
12. When the French Empire was founded in North America, contact with European culture had profound effects on the Amerindians.Which of the following statements show the impact that Europeans had on the Amerindians of that time?
1. The native peoples could use goods made with iron or steel.
2. The native peoples learned techniques for survival in the bush.
3. The native peoples were introduced to alcohol.
4. The native peoples were introduced to the use of tobacco and medicinal plants
5. The native peoples were exposed to new diseases.
6. The native peoples discovered new foods such as corn and maple syrup.
A) 1, 3, and 5
B) 1, 4, and 6
C) 2, 3, and 4
D) 2, 5, and 6
13. Which of the following show the influence of European cultural practices on the Amerindian way of life during the 17th century?
1. the establishment of Christianity by the missionaries
2. the regular use of tobacco in ceremonies
3. the use of iron and metal in tools
4. the adoption of light means of transportation suited to the climate
5. the affiramtion of maternal authority within the family structure
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 4
C) 2 and 5
D) 3 and 4
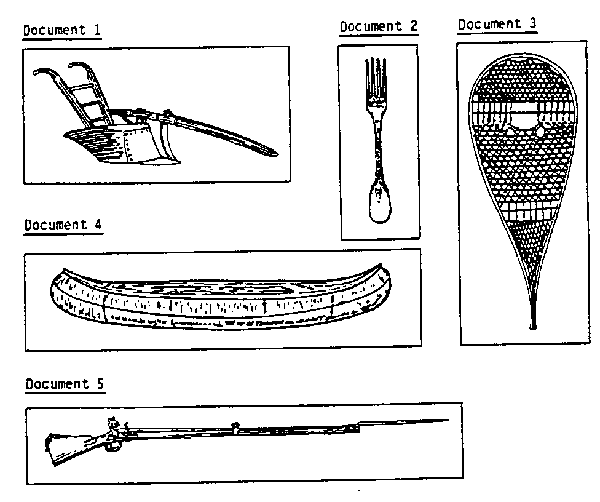
14. Europeans learned much from the Amerindians and borrowed several things from their way of life.Which of the following illustrations show examples of Amerindian influence?
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 3
C) 2 and 5
D) 3 and 4
15. The arrival of the Europeans and their culture transformed the life of the native peoples of North America. They quickly adopted such European commodities as copper kettles, metal tools, weapons, textiles, and foods such as baked bread. For their part, the Europeans were influenced by the cultures of the native peoples, and readily adopted native products such as:
1. alcohol
2. birch-bark canoes
3. moccasins
4. snowshoes
5. salt
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 1, 2, and 5
C) 2, 3, and 4
D) 3, 4, and 5
16. Throughout the French Regime, the fur trade constituted the main economic activity of New France. Contrary to popular belief, the Amerindians did not part with their trapping income carelessly.For which of the following goods did the Amerindians trade their furs?
1. snowshoes
2. firearms
3. metal tools
4. canoes
5. blankets
A) 1, 2, and 4
B) 1, 3, and 4
C) 2, 3, and 5
D) 3, 4, and 5
17. Amerindians and Europeans learned from each other.Which of the following did the early European settlers adopt from the Amerindians?
1. wool blankets
2. corn
3. tobacco
4. iron pots
5. bread
A) 1 and 4
B) 1 and 5
C) 2 and 3
D) 4 and 5
THIS TEST IS ON: MODULE I: "THE FRENCH EMPIRE IN NORTH AMERICA"
UNIT 3: AMERINDIAN CIVILIZATION
TOPIC A: SOCIO-CULTURAL ORGANIZATION
TOPIC B: MUTUAL INFLUENCES
1. Ans: B Diff.: 1 Page: 91-6-2 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........7
2. Ans: D Diff.: 1 Page: 91-6-23 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........8
3. Ans: D Diff.: 1 Page: 91-8-1 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........9
4. Ans: C Diff.: 1 Page: 87-6-2 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........10
5. Ans: A Diff.: 1 Page: 87-6-3 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........11
6. Ans: A Diff.: 1 Page: 88-1-1 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........12
7. Ans: D Diff.: 1 Page: 89-1-3 Refer To: 0109
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........13
8. Ans: B Diff.: 1 Page: 89-8-3 Refer To: 0110
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........14
9. Ans: A Diff.: 1 Page: 90-1-3 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........15
10. Ans: C Diff.: 1 Page: 90-6-3 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........16
11. Ans: B Diff.: 1 Page: 90-1-1 Refer To:
Topic: ORGANIZATION 3A
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 ........17
12. Ans: A Diff.: 1 Page: 113 Refer To:
Topic: INFLUENCES 3B
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........1
13. Ans: A Diff.: 1 Page: 88-6-4 Refer To:
Topic: INFLUENCES 3B
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........2
14. Ans: D Diff.: 1 Page: 89-1-1 Refer To: 0108
Topic: INFLUENCES 3B
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........3
15. Ans: C Diff.: 1 Page: 89-1-5 Refer To:
Topic: INFLUENCES 3B
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........4
16. Ans: C Diff.: 1 Page: 89-8-5 Refer To:
Topic: INFLUENCES 3B
File: M1U3 UNIT 3 .........5
17. Ans: C Diff.: 1 Page: 90-1-5 Refer To:
Topic: INFLUENCES 3B